Overview
Data is the most valuable asset and resources second to human that any organization must manage. Data management determines organizations profitability and survivability:
-
- Profitability: An organization makes profit when information and resources are well managed and a loss can ruin an organization business.
- Survivability: Organization that mismanage its data and resources will suffer loss, which may cause it never to earn a profit or even survive.
Therefore, data risk management should start with classification and categorization:
-
- Classification: Helps to determine the level of protection that should be given to data. Common classification is Proprietary, Private, Classified, or Public. However, in the government, data is classified as Top Secret, Secret, Confidential, and Unclassified.
- Category: Helps to inform the way data is used or store. Common categories are data in motion, data at rest and data in use (memory/cache)
- The danger with data will mainly come from data leakage. A leak can affect the organization’s profitability and survivability.
As increasingly connectivity and mobility offer some significant benefits to organizations, many executives are left wondering how to prevent data leak from the different mobile silos where they are resident. Regardless of where the data is in the mobile device or whether it includes device information or schematics, a salesperson’s contacts, or a single stock code, data leakage can be very damaging to an organization. Preventing or limiting leakage, while still rolling out and deploying mobile devices, is increasingly becoming more challenging as more and more businesses embrace new mobile device or storage technologies, solutions, and products.
Another complicating factor is the corporate adoption of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD). The rise, and “consumerization of IT,” BYOD policies, coupled with the rise of distributed data access across end-user devices, and the Cloud entails a deluge of data that is difficult to downrightly - if not impossible - to know where the data resides and who owns the device it resides on.
Given the above, it is evident that organizations should approach mobile data leakage on three fronts:
- Protecting data inside the organization from leakage
- Protecting data on mobile devices (whether employee- or company-owned) from leakage; and
3. Preventing corporate apps from mishandling enterprise data on employee devices
Ownership and Residency
Broadly speaking, the ownership and residency are key factors when deciding how to provide protecting against data leak. Primarily there are three (3) categories:
- Sole Ownership: Mobile device and data is owned by the organization and resides in the organization’s controlled facilities
- Contracted or Delegated Ownership: A third party is handling the device and data, or just the residency i.e. data backed up in the Cloud, or
- Mixed Ownership: Mobile device is owned by an organization but managed by individual employees. In this case, the organization has implemented requirements to ensure that employees cannot be the cause of a leak by them merely having access to sensitive data.
Regardless of ownership type or residency data leakage does not exist in isolation and there are key security measures that must be provided to prevent data leakage. A defense-in-depth approach is required to provide protection in a layered fashion. It is also important to note, that due to variations in the manner of implementations of BYOD in organizations, there might not be a “One-fit-all” model of security in which case due diligence takes a center stage regardless of ownership/control model.
Impact of Data Leakage
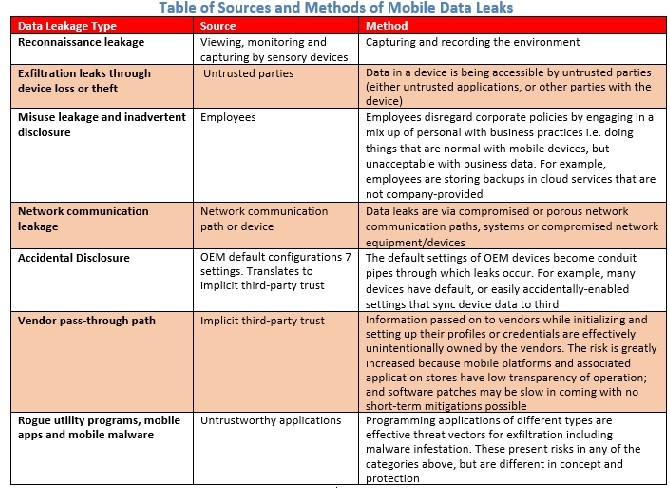
There are different types of impacts that an organization can experience when data leaks out or is exfiltrated from a mobile device.
Given in the Table are pertinent characteristics associated with mobile data exfiltration or leakage. It is important to note that device types and its underlying security protection design and mechanism will very likely determine to what extent and how preventive measures can be applied.
Summary
Data leakage prevention is increasingly gaining attention as companies try to deploy new security measures to protect sensitive data that are stored, processed or transmitted on mobile devices.
Invariably, the most effective way to prevent data leakage is to support an ongoing process with an all-out approach that is all-inclusive and planned. The following are some tangible steps you can take to prevent data leakage:
- Establish tools and processes that track your data's movement so you know where it is stored, how it is accessed, and who is using it.
- Identify the types of data that require a unique protection regime within and beyond your company's walls.
- Consider new security approaches for next-generation tools and capabilities that addresses the security issues of data leaks and exfiltration.
Employees should understand and implement basic security procedures:
-
- Protect systems by using only authorized application and access methods, maintaining security software such as antivirus applications, respecting and maintaining security settings.
- Protect portable devices by keeping them in your possession or locked up at all times, not sharing your work devices or using them for personal activities, not forwarding confidential information from work systems to personal devices, and not accessing inappropriate sites or downloading inappropriate information.
- Prevent unauthorized data access by logging off or locking systems when you walk away for a few moments or leave for the evening, using sound password creation techniques and not sharing passwords, and storing passwords securely
- Prevent data theft while traveling by speaking softly when you must discuss confidential information in public, using privacy filters to prevent over-the-shoulder viewing, using a VPN, and never using a business printer unless you are there to pick up the paper
Employees must understand that they play a critical role in maintaining corporate security and accept responsibility and accountability for protecting the enterprise. Each employee should:
- Conduct daily business activities according to the company's code of business conduct- particularly those pertaining to information security.
- Be constantly aware of their surroundings and conscientious about security in every action they take in the office, at home, and on the road.
- Learn how to handle the different levels of confidentiality for their company's documentation. This includes understanding the differences between "public," "confidential," "highly confidential," and "restricted
About Unatek
Unatek is a trusted provider of security research and advisory services to Fortune 2000 enterprises and government agencies. Unatek Advisory and Security Services help organizations address security, compliance, operational risk and IT risk challenges. As recognized experts and thought leaders in the field of security, Unatek consultants deliver solutions that fit the customer’s organizational maturity, business requirements and existing technology investments.
Contact Us
For more information on Unatek products and services, visit www.unatek.com, email us at sales@unatek.com or call +1 301.222.0734.